Dougal Dixon's After Man: A Zoology of the Future features numerous life forms that are the counterparts of real ones, both living and extinct. This includes the following:
- Rabbucks are rabbit-descendants resembling ungulates, complete with hooves. Those living on temperate climates are similar to deer, whereas tropical ones resemble antelopes and zebras (the zebra-like version is named strank). One species, the picktooth, evolved large tusks, filling the ecological niche of warthogs.
- Luties are also rabbit-descendats that went the opposite way, shrinking in size and filling in the niche of mice and voles (despite coexisting with regular rodents).
- Rat-descendants take the place of large carnivores, including wolves (falanx), cheetahs (rapide), weasels (janiset), foxes (temperate and polar ravenes), polar bears and sabretooths (bardelot) and even walruses (distarterops) and sea lions (pytheron). Lacking canine teeth, it's their incisors that evolved into sharp killing teeth (similarly to the real-life prehistoric carnivorous marsupials in the family Thylacoleonidae).
- Weasel descendants took over the niches of some larger carnivorous mammals in remote places where predatory rats couldn't establish themselves, including the wolf-like pamthret and the snow leopard-like shurrack (the latter even has snow leopard rosettes).
- The shrock is virtually identical to a badger, though descended from small insectivores.
- The reedstilt is, bizarrely, a mammalian heron, a fish-eater with long neck and snout, living in reed beds.
- Some squirrel-descendants, even more bizarrely, take the niche of insects: the chirit moves on branches like an inchworm, whereas the chiselhead gnaws tree-trunks like a beetle larva. Shrews also have a few insect-like descendants, including the pfrit that runs on water like a water strider bug and the trovamp, a blood-sucker similar to ticks.
- The tree drummer is a temperate-dwelling shrew descendant that is morphologically similar to an aye-aye that uses its tongue rather than its fingers to fish out insect larvae from wood.
- Gigantelopes are large, rhinoceros-like mammals descended from antelopes. They come in hairless tropical and wooly boreal variants. Hornheads, their close relatives, are similar in size, shape and ecological niche to moose.
- Raboons are bipedal, carnivorous baboon-descendants behaving like theropod dinosaurs, with smaller raptor-like and large, Tyrannosaurus rex-like variants.
- The horrane is a predatory simian that converged with various big cats. It has the lanky build of a cheetah, the mane of a lion, and the horizontal stripes of a tiger. It also hunts by slashing larger prey animals with its claws like dromaeosaurs were once envisioned to have done.
- The vortex and porpin are penguin-descendants resembling cetaceans. The former is a giant filter-feeder like a whale, while the latter is an agile fish-hunter like a dolphin.
- The flunkey is a monkey with flying membranes similar to a flying squirrel.
- Tropical pig-descendants include the elephant-like zarander (a large, long-trunked herbivore) and the anteater-like turmi (a long-tongued insectivore).
- The mud-gulper is a large aquatic herbivore similar to a manatee, but with a hippopotamus-like head, descended from aquatic rodents.
- Australia has a number of marsupials taking the place of tropical animals, including the tapir-like posset, the monkey-like chuckaboo and the sloth-like slobber, as well as the giantala, a ground sloth-like kangaroo-descendant.note
- In South America, the gurrath is a jaguar-like mongoose (complete with rosette-like pattern). Its prey, the tapimus, is a tapir-like rodent.
- The birds of Pacau all evolved from the Australian golden whistler, but went through a massive diversification. This includes the woodpecker-like insect-eater and the raptor-like hawk whistler.
- The bats of Batavia include the surfbat (a chiropteran seal) and the shalloth (a sloth-equivalent, although with more varied diet).
- The desert leapers of Asia are gerbils that resemble large kangaroos but fill the ecological niche of camels.
- The khilla is similar to a wolf, coyote, or jackal, descended from insectivores.
- The grobbit is a hoofed rodent that sometimes stands on its hind legs to reach branches, much like a gerenuk
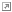 .
. - The testadon is an armadillo-analogue (though its mechanism is actually closer to a pillbug) descended from hedgehogs.
- The spine-tailed squirrel is the future's version of a porcupine or hedgehog, though its coloration is reminiscent of a skunk.
- Averted with the beaver, which is just a regular beaver with a few evolutionary changes, filling the same niche. The meaching, a lemming-descendant, also fills the same niche as its ancestor.
